This is the text of a detailed letter I am sending to my representatives and other leaders in Albany. I invite anyone to use any portion of it and the resources in the notes to write your own. However, the New York State Allies for Public Education has a convenient web form that will generate a letter to your representatives as well. It can be found here. The agenda has been set by Governor Cuomo and Chancellor Tisch — it will make our schools objectively worse in every way and it will sweep up all teachers regardless of their capabilities. We need parents, community members, and teachers to band together to say that this must be stopped. Let’s dare our representatives in Albany to become friends of public education.
The Honorable Linda Rosenthal
LOB 741
Albany, NY 12248
Senator Jose Serrano
181 State Street Room 406
Legislative Office Building
Albany, NY 12247
Dear Assemblywoman Rosenthal and Senator Serrano:
The public schools of New York need some friends in Albany.
I wish I could say that the parents, children, and teachers of this state could count upon friendship in the Governor’s office or at the Regents Chancellor’s office, but both Governor Cuomo and Chancellor Tisch have made it very clear that they intend great harm to our public education system. They have powerful backers among Wall Street and private foundations, and they have the encouragement of the United States Department of Education, but regardless, what they say they intend to do will not only harm the 600,000 public school teachers of New York, but also it will degrade the quality of education enjoyed by millions of school aged children and counted upon by their parents and communities.
Governor Cuomo vetoed a bill on December 29th that his own office drafted (1) and which would have given teachers and principals a two year grace period from suffering professional consequences due to the results of the new Common Core aligned state examinations. The Governor justifies this by claiming that the current teacher evaluation system finds too few teachers incompetent and that student scores of the new exams demonstrates that this is untrue. Chancellor Tisch has joined the Governor in calling for far more rigid teacher evaluations, responding to a December letter from the State Director of Operations with her own priorities. (2) Chancellor Tisch backs changing teacher evaluations so that the 20% currently set aside for local measures of teacher performance be eliminated and that the portion assigned to student growth in standardized tests be raised to 40% overall. In addition, Chancellor Tisch proposes that a teacher found “ineffective” by the standardized tests be determined to be ineffective overall, and she believes that two such evaluations should lead to a teacher’s removal.
There are few proposals that could be so immediately harmful to students regardless of Governor Cuomo’s declaration that he is looking out for them and that the NYSUT only wants to protect bad teachers. This change to teacher evaluation rests upon a flawed premise about student achievement in New York, will subject teachers to an evaluation system with no basis in research, and will dramatically harm the quality of curriculum and instruction across the state in both affluent and impoverished districts.
Governor Cuomo and Chancellor Tisch apparently believe that because the student proficiency levels on the new Common Core aligned examinations are in the 30-35% range then it is “obvious” that many more New York teachers must be incompetent and deserve to be removed from the classroom. This is a flawed premise and deliberately misleading. Both the Governor and Chancellor know full well that the cut scores for proficiency were set deliberately to match SAT scores (3) linked to specific grades in first year college courses. The percentage of New Yorkers over 25 with a bachelor’s degree is 32.8 (4),so the argument that THESE proficiency levels on THESE exams mean that many New York teachers are incompetent only works if you assume that there is a demand for college educated workers not being met currently. The economic evidence for that assumption is weak, however, because while a college wage premium exists, its growth has shrunk dramatically in recent decades (5) and much of that small growth is coming from falling wages for non-college graduates. It would be worthwhile to question the uneven distribution of college opportunity among racial, ethnic, and economic lines, but it would also be worthwhile to discuss the loss of opportunities for families to move from poverty to the lower middle class (6), losses that keep many more families in poverty than can be lifted by more college degrees.
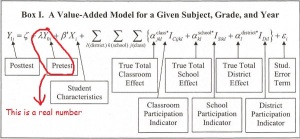
From that flawed premise, Governor Cuomo and Chancellor Tisch assume that teachers can be accurately measured as ineffective based upon standardized test scores. Nothing could be further from the truth. Value Added Models (VAMs) are not widely accepted as valid for teacher evaluation, and the evidence against using them that way led the American Statistical Association to issue a statement warning about the limitations of VAMs (7). Teacher ratings using VAMs can be highly unstable. Dr. Bruce Baker of Rutgers notes that teachers who ranked in the top 20% of teachers using value added modeling were likely to shift in subsequent years (8), some even to the lowest quintile and then back to the top, demonstrating how unreliable these methods are. VAMs take their toll on excellent teachers in excellent schools as well, as demonstrated by the case of the “worst 8th grade math teacher in New York City” in 2012 (9). This teacher taught at a citywide gifted and talented school, and all of her students passed the challenging Regents algebra exam, but her VAM, based upon an exam testing material her students had learned several years earlier, placed her at the absolute bottom of all 8th grade math teachers. Hers is not an isolated case, and if Governor Cuomo and Chancellor Tisch have their way, there will be no locally derived measure sufficient to have saved her job.
The tragic impact this will have upon classrooms everywhere should be obvious. With such dire consequences tied to a single set of standardized examinations and with no other measure mattering, teachers, even in successful schools, will have to teach to the test. Narrow and relentless test preparation can increase student scores, but it comes at the expense of creativity and subjects not tested. Research since the passage of No Child Left Behind demonstrates that subjects such as science, social studies, art, music, and physical education have all been reduced because of the consequences attached to low test scores (10). The Cuomo/Tisch proposals for teacher evaluation will inevitably accelerate this, leading to less time spent in a well rounded curriculum and more time in didactic instruction and seat work.
Meanwhile, the New York Times recognized this week that fiscal inequity is “the central crisis” in New York’s schools, and that Albany is over $5.6 billion dollars short annually of commitments made in 2007 (11). The New York State School Boards Association estimates that the average district in New York has lost $3.1 million a year in state aid due to the continued use of the gap elimination adjustment (12), and Dr. Baker of Rutgers calculated that New York City alone has lost between $3-4000 per pupil per year through Albany’s refusal to fully fund its own aid formula (13).
In a time when teachers are being told to do far more with their students, Governor Cuomo has consistently starved local districts of funds, and now he and Chancellor Tisch demand that these same teachers produce test results or be fired using statistical models with no foundation in research.
Enough is enough. The New York State Allies for Public Education has responded to Governor Cuomo and Chancellor Tisch (14), and I implore you to join them in opposing this damaging agenda. It has no basis in fact, it will severely harm all of our schools in every community, and it fully ignores the ongoing failure of Albany to equitably fund our state’s schools.
Our public schools need friends in Albany. I hope that you will be among them.
Sincerely,
Daniel S. Katz, Ph.D.
Director of Secondary Education and Secondary/Special Education, Seton Hall University
Father of Two New York Public School Students
Notes:
1. Taylor, K. (2014, December 29). Cuomo Vetoes Bill That Would Protect Teachers From Low Ratings. The New York Times. Retrieved January 6, 2015, from http://www.nytimes.com/2014/12/30/nyregion/cuomo-in-reversal-vetoes-bill-that-would-have-protected-teachers-from-low-ratings.html
2. Burris, C. (2015, January 1). Teacher Evaluation: Going from Bad to Worse? The Washington Post. Retrieved January 6, 2015, from http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/answer-sheet/wp/2015/01/01/teacher-evaluation-going-from-bad-to-worse/
3. Burris, C. (2014, April 29). The Scary Way Common Core Test “Cut Scores” Are Selected. The Washington Post. Retrieved January 5, 2015, from http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/answer-sheet/wp/2014/04/29/the-scary-way-common-core-test-cut-scores-are-selected/
4. United States Census Bureau. (n.d.). Retrieved January 7, 2015, from http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/36000.html
5. Shierholz, H., & Mishel, L. (2013, August 21). A Decade of Flat Wages: The Key Barrier to Shared Prosperity and a Rising Middle Class. Retrieved January 7, 2015, from http://www.epi.org/publication/a-decade-of-flat-wages-the-key-barrier-to-shared-prosperity-and-a-rising-middle-class/
6. Harris, B., & Kearney, M. (2013, December 4). A Dozen Facts about America’s Struggling Lower-Middle-Class. Retrieved January 7, 2015, from http://www.brookings.edu/research/reports/2013/12/12-facts-lower-middle-class
7. ASA Statement on Using Value-Added Models for Educational Assessment. (2014, April 8). Retrieved January 7, 2015, from https://www.amstat.org/policy/pdfs/ASA_VAM_Statement.pdf
8. Baker, B. (2012, November 17). On the Stability (or not) of Being Irreplaceable. Retrieved January 7, 2015, from http://schoolfinance101.wordpress.com/2012/11/17/on-the-stability-or-not-of-being-irreplaceable/
9. Pallas, A. (2012, May 16). Meet the “Worst” 8th Grade Math Teacher in New York City. The Washington Post. Retrieved January 6, 2015, from http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/answer-sheet/post/meet-the-worst-8th-grade-math-teacher-in-nyc/2012/05/15/gIQArmlbSU_blog.html
10. David, J. (2011). High Stakes Testing Narrows the Curriculum. Educational Leadersip, 68(6), 78-80. Retrieved January 6, 2015, from http://www.ascd.org/publications/educational_leadership/mar11/vol68/num06/High-Stakes_Testing_Narrows_the_Curriculum.aspx
11. The Central Crisis in New York Education. (2015, January 4). The New York Times. Retrieved January 6, 2015, from http://www.nytimes.com/2015/01/05/opinion/the-central-crisis-in-new-york-education.html?_r=1
12. Q&A: New York State’s Gap Elimination Adjustment. (n.d.). Retrieved January 7, 2015, from http://www.nyssba.org/clientuploads/nyssba_pdf/Q&A/Q&A-Gap-Elimination.pdf
13. Baker, B. (2012, December 7). Forget the $300m Deal! Let’s talk $3.4 billion (or more)! Retrieved January 7, 2015, from http://schoolfinance101.wordpress.com/2012/12/07/forget-the-300m-deal-lets-talk-3-4-billion-or-more/
14. NYSAPE Response Letter to Governor on Public Education. (2015, January 5). Retrieved January 7, 2015, from http://www.nysape.org/nysape-response-letter-to-governor-on-public-education.html